
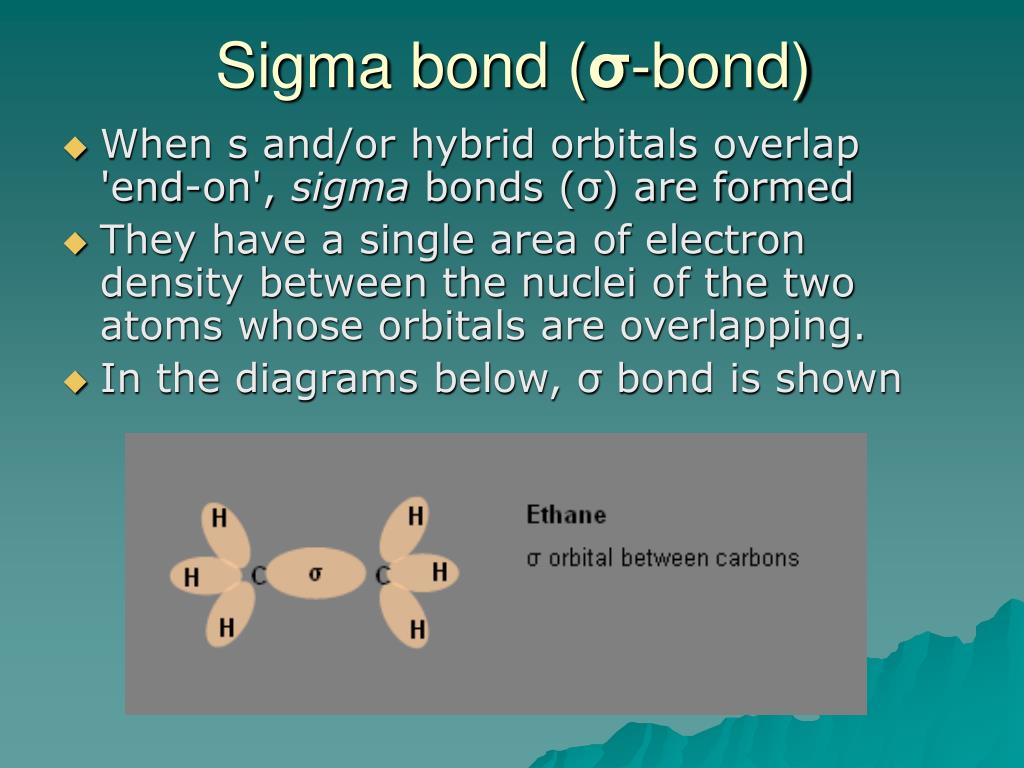
The pi bond (π bond) has two halves-one above the plane of the molecule, and the other below it. This is called a pi bond, Greek letter π. A second carbon-carbon bond is formed by the overlap of these two remaining p orbitals. The sp2 hybrid orbitals on each carbon atom involve the 2 s and two of the 2 p orbitals, leaving a single 2 p orbital on each carbon atom. By selecting N8 HOMO, you can see the pi orbital represented by the two lobes. This is actually sigma bonding between C-C and some sigma-like bonding around the Hs as well. To view the sigma bonding orbital, select N6. These overlap sideways to form a π bond, also shown in gray. Two p orbitals, one on each C atom, are shown in gray. Two of these overlap directly between the carbon atoms to form the σ bond. Three sp 2 hybrids around each carbon atom are indicated in color.

Similar to this, the triple bond between the nitrogen atoms in N 2 gas is made of one sigma and two pi bonds.\) The sigma-pi model of a double bond.
For example, in carbon dioxide, CO 2, each single between the carbon and oxygens is a sigma bond, and there is a pi bond making two C=O double bonds: The principle of identifying sigma and pi bonds is applicable to any molecule, be that smaller or large than what we have discussed so far. * In a triple bond there is one σ (sigma) and two π (pi) bonds. * The angle between atoms is 180 o – linear geometry. The key parameters of the sp hybridization and triple bond: The two p orbitals of each carbon overlap to make two π bonds. One hydrogen bonds to each carbon atom by overlapping its s orbital with the other sp orbital. For example, in acetylene, C 2H 2, the carbons are connected with a triple bond in which one is a sigma bond formed by the head-on overlap of the two sp orbitals and two pi bonds which are formed by overlapping two pairs of p orbitals: This results in what is called the cis and trans isomerism in alkenes which, again, we will talk about in organic chemistry.Īs a shortcut to recognizing the sigma and pi bonds, you can remember that in multiple bonds (double or triple), there is always one sigma bond, and the remaining are pi bonds.
#Describe one type of a sigma bond free#
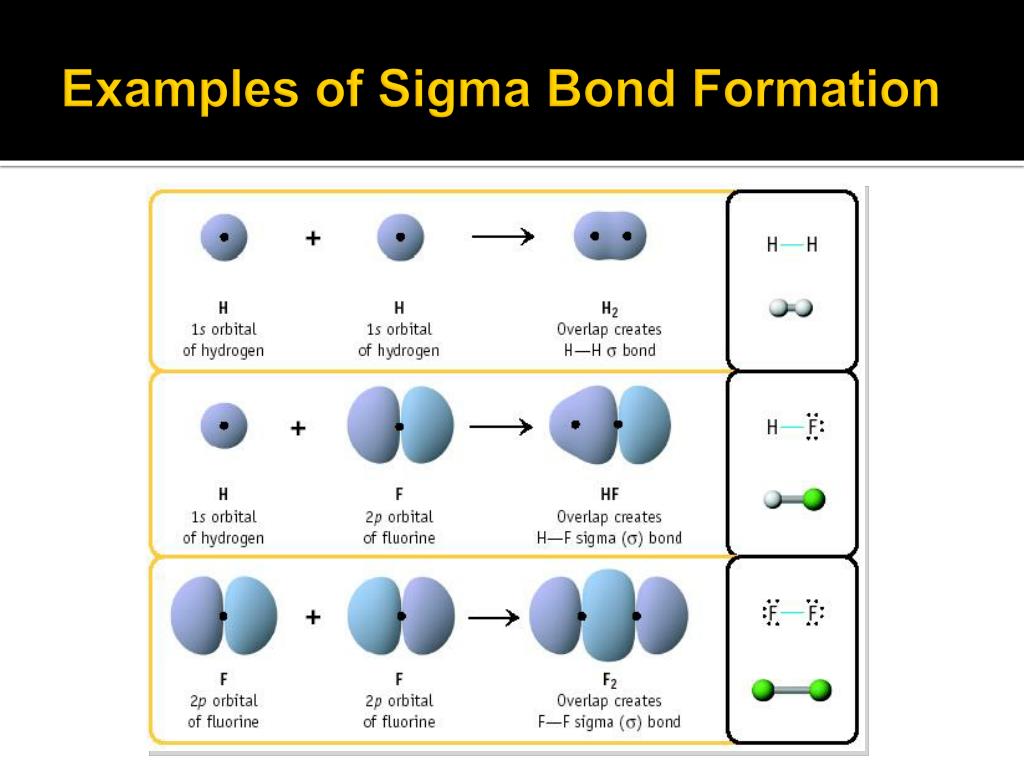
This is why in organic chemistry, you will see reactions involving breaking pi bonds far more often than sigma bonds as they are broken much easier.Īn interesting feature distinguishing sigma and pi bonds is the former is characterized by free rotation about the bond axis, while the presence of a pi bond restricts this, and the atoms are locked in their position relative to the double bond. The side-to-side orbital overlap allows a less efficient electron sharing, and therefore, p bonds are generally weaker than sigma bonds. * The angle between the plane and p orbitals is 90 o. * All the atoms on the double bond are in one plane. Here are some key parameters about the sp 2 hybridization and double bonds that you need to know: In each double bond, there is one sigma and one π bond. So, the two carbons in ethylene, which is the first member of the alkene family, are double-bonded. The two carbons are sp 2-hybridized where the sp 2 orbitals overlap to form the sigma bond, and the unhybridized p orbitals form the pi bond. The pi bond is formed by a side-to-side overlap of two p orbitals provided by adjacent atoms. On the other hand, in ethene, or ethylene (C 2H 4), there is one sigma and one pi bond between the two carbon atoms: For example, the single bond between the two carbons in ethane (C 2H 6) is a sigma bond because it is formed by overlapping two sp 3 orbitals of the adjacent carbon atoms: In short, you can remember that single bonds are sigma bonds. The bonds that form by the head-on overlap of orbitals are called σ (sigma) bonds because the electron density is concentrated on the axis connecting the two atoms. Now, there are two types of covalent bonds: sigma ( σ) and pi (π) bonds. We mentioned in the previous post that covalent bonds are formed as a result of sharing two valence electrons in overlapping orbitals of two atoms.įor example, the following Lewis structures represent covalent bonds together with some lone pairs of electrons:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
